Attention all lovers of nature, amateur astronomers and night owls: the night of the 27th of July, 2018 will be totally different. In this particular night, we will experience the Opposition of Mars and a rare Total Lunar Eclipse in Europe! It is sure to be a midnight Summer dream, in the middle of warm temperatures and mystical experiences.
In this article, you will learn about, that which you can use to observe and photograph the Total Lunar Eclipse and Mars.
Another interesting point: currently, there are a number of other planets to see. Now is the perfect opportunity to jump into Astronomy. You will be rewarded with a fireworks show of planets. Mars, Jupiter, Venus and Saturn are waiting for you to rediscover them!
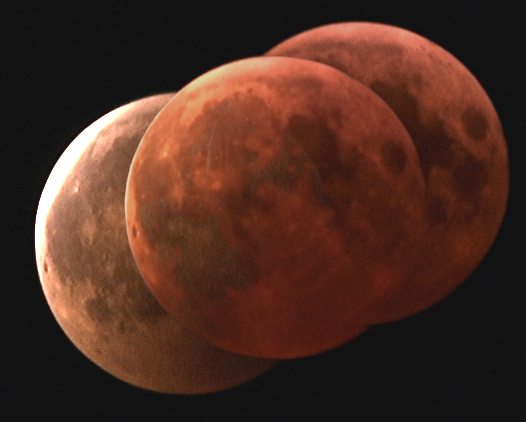

As the night slowly falls, the Moon will rise in the southeast. Our satellite will look unusual and simultaneously fascinating. Almost completely eclipsed, it will rise higher and higher. The “blood Moon”, which evoked fears and superstitions of death and destruction in earlier times, will be visible for us to witness with our knowledge and science in a relaxing manner and with a smile.
The highlight of this year: at a length of 1 hour and 44 minutes of totality, we will get to enjoy the longest Lunar Eclipse of the century! More information about this event is available below.
Now you can read on to learn about the 5 ways and effective products, to observe the Moon and the Planets. Let’s go!
1. Discover the Sky with Binoculars
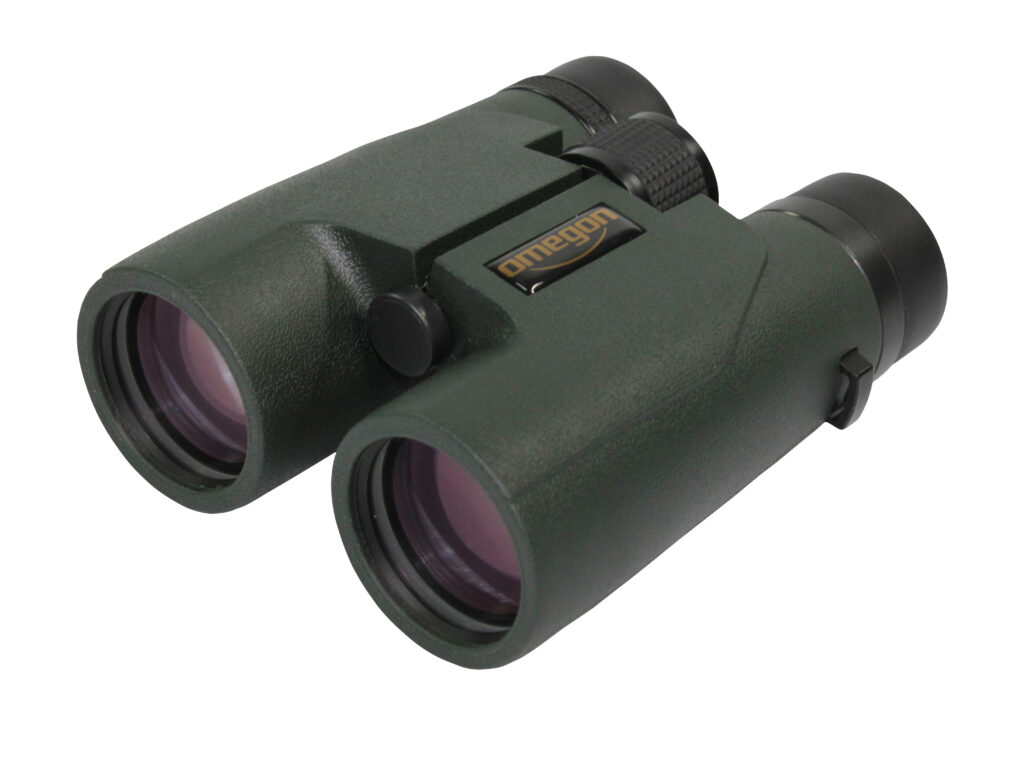
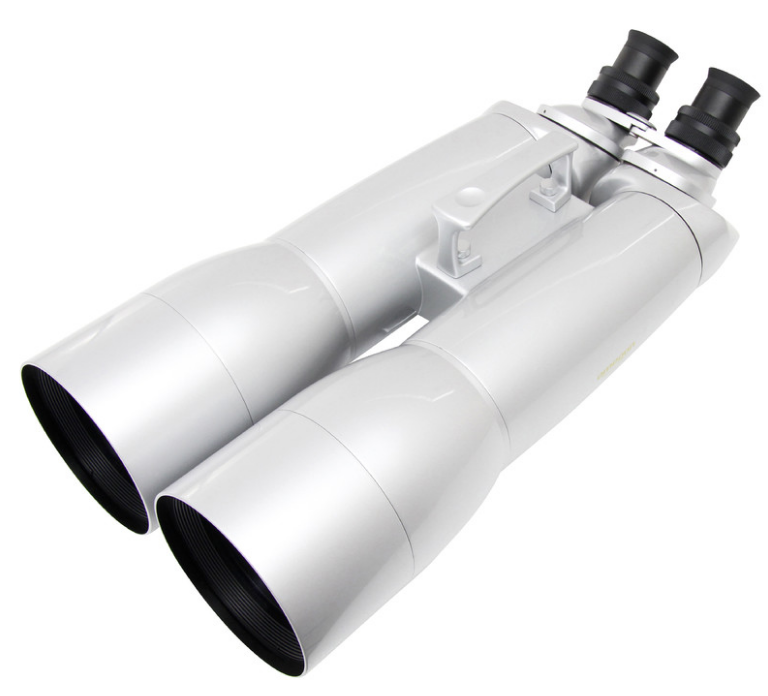
The lunar eclipse is visible with the naked eye, but with a pair of binoculars, the Moon in the Earth’s shadow becomes an especially intense experience. For an great observation, we recommend the Omegon Binoculars Nightstar 20×80. These binos are a great alternative to a telescope or as an entry into Astronomy. They are bright and something that you can always carry with you. Just point the binos to the sky or mount them on a tripod. Then you will see the Moon in all its glory and innumerable craters. It is amazing with both eyes, as if you were there. But there is more. You can can even view Jupiter and its moons as well as starclusters, such as the Pleiades or the Andromeda Galaxy.
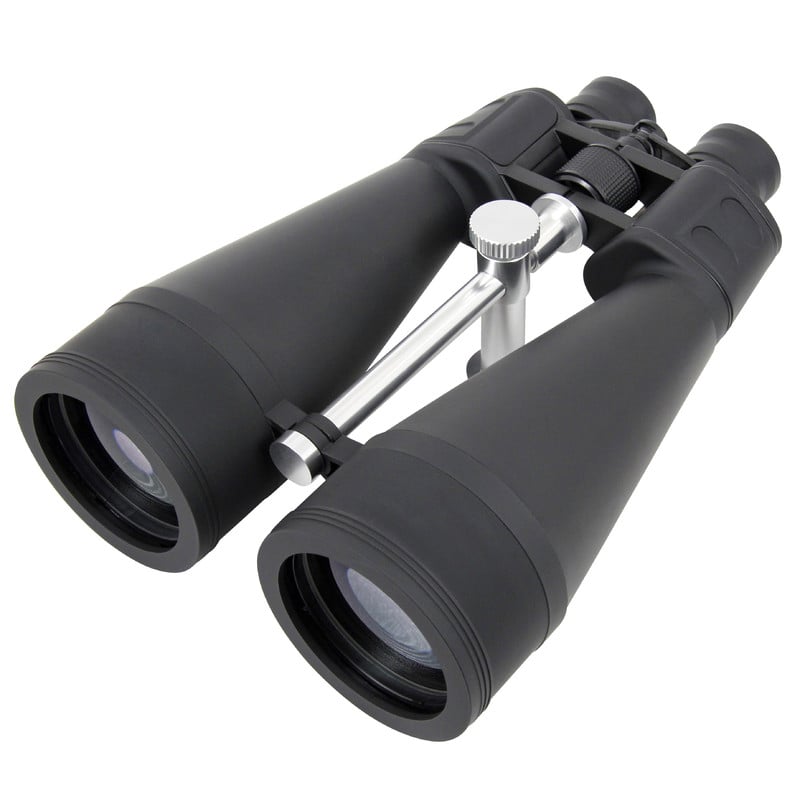

The Omegon Binoculars 20×80
2. Getting closer with a telescope
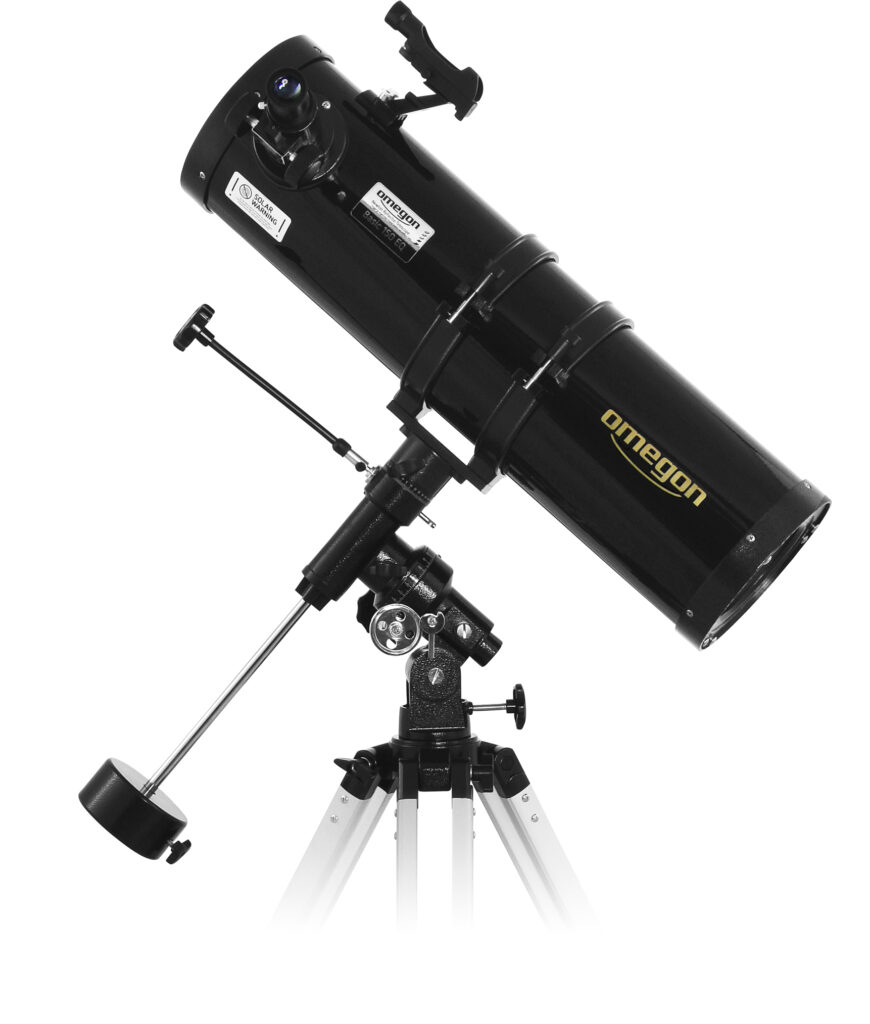
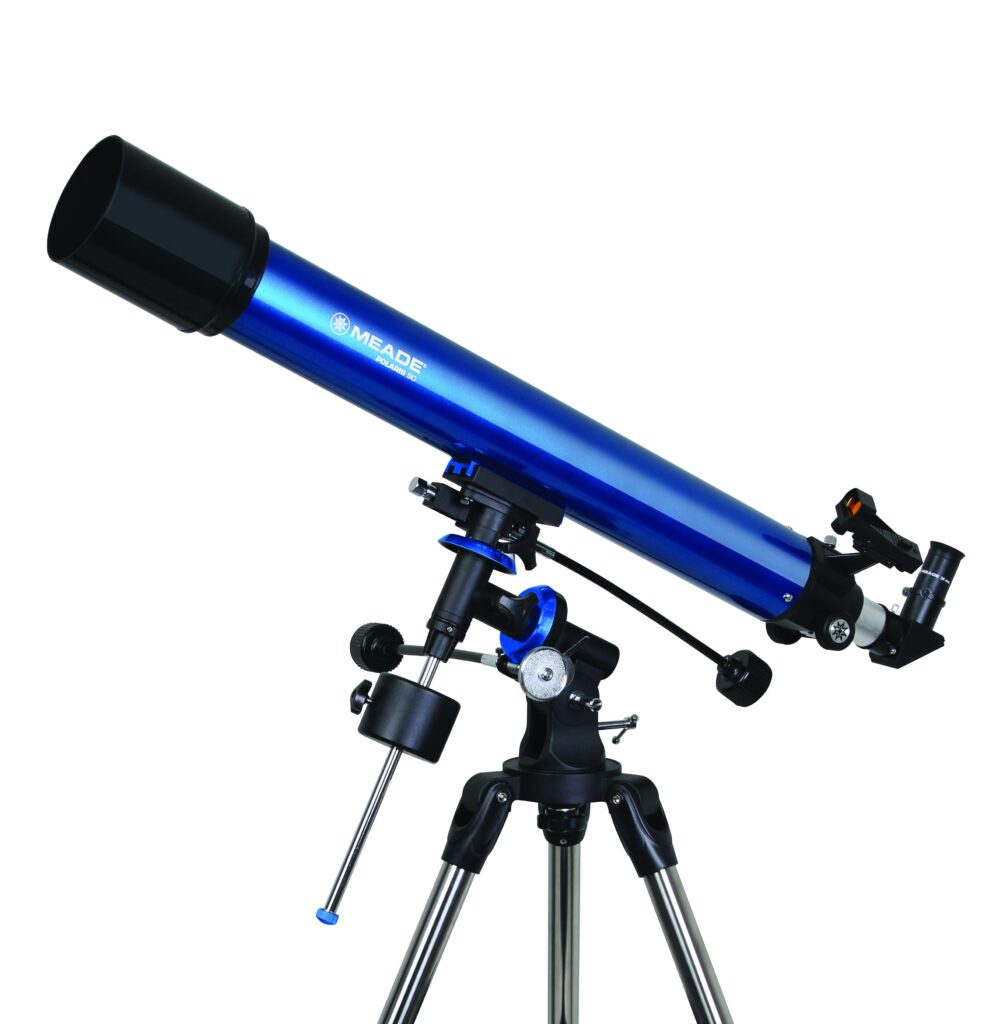
Much like a mega zoom into the cosmos: A telescope allows you to see real detail. Observe the entire Moon, singular lunar craters, Jupiter, or Saturn with its massive system of rings. However you want. The possibilities are endless! With a greater magnification, only available with telescopes, you will be able to see Mars for the planet that it is and not just the red “star” in the night sky. The Omegon AC 70/700 AZ-2 is the most budget-friendly entry point. With a 70mm aperture, it collects 100 times more light than the naked eye. The eyepieces enable a 35x and 70x magnification, or in combination with a barlow lense up to 140x. More details and more resolution is available in the Omegon AC 90/1000 EQ-2. The telescope is our tip for entry into lunar and planetary observing. With a 90mm aperture, you will be able to see many details, such as the cloud bands on Jupiter or the polar caps on Mars.
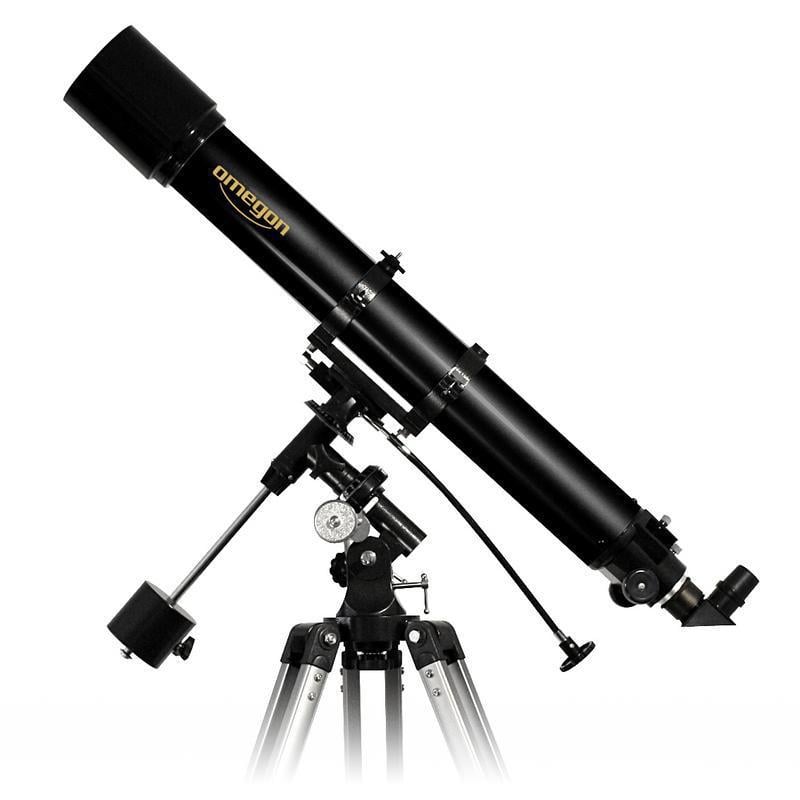

The Omegon AC 90/1000 EQ-2 – Recommendation for entry into Astronomy
3. The simplest way to your own astrophotos
A photo of the lunar eclipse? It’s possible with the simplest tools.
With a telescope, the path to your own photos is just a small step. The best camera for such a task is right in your pocket: your smartphone! Pick up a Smartphone adapter, which will keep your phone perfectly positioned above the eyepiece. We also offer the more budget-friendly Omegon Smartphone Adapter, which demands a bit of finesse or the Omegon Easypic Universal. This smartphone adapter is a self-centering and easy-to-use device. It only takes one minute and you will already have taken your own lunar photo.
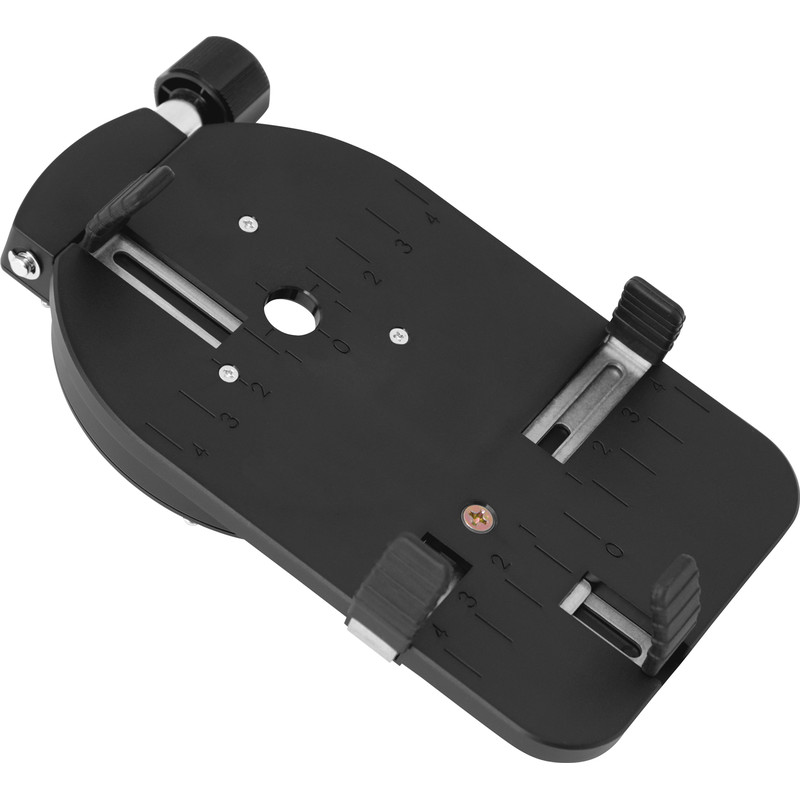

Omegon Easypic Universal Smartphone adapter
4. The right eyepiece is decisive, when it comes to details
With eyepieces, you often must separate the wheat from the chaff. An eyepiece is essentially an extended arm of the telescope’s optic and you should put a lot of stock into selection, just as you would with a telescope itself. A good tip would be to replace old or standard eyepieces with high quality ones, which can provide you with a significantly better image. Excellent crispness and great contrast can be found in the Omegon LE Planetry Eyepieces for all 1,25“. The customer reviews range from “just fantastic” to “you cannot believe it”.
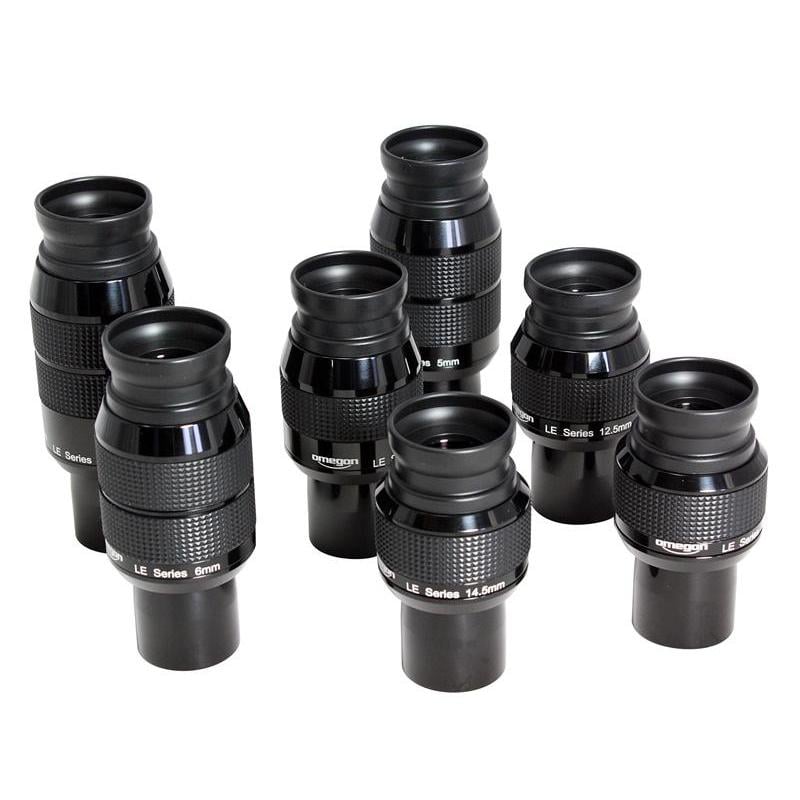

The Family of Omegon LE Planetary Eyepieces
5. Color filters for better contrast
Much like a chain, the planets of Venus, Jupiter, Saturn and Mars will appear to us in a line, and all after darkness has fallen, during the most comfortable time of year. The constellation of planets is so rare, that now is the time to jump into astronomy. Amateurs can easily pinpoint the planets and see details of each. Polar caps and other structures on Mars, or the big red dot on Jupiter become more visible with the appropriate color filters. Placed into the eyepiece, filters can lead to an epiphany for any motivated observer. The Omegon Color filter set features the most important ones for all planets. Other contrast filters or our Lunar Filter are also a helpful inclusion to your collection.
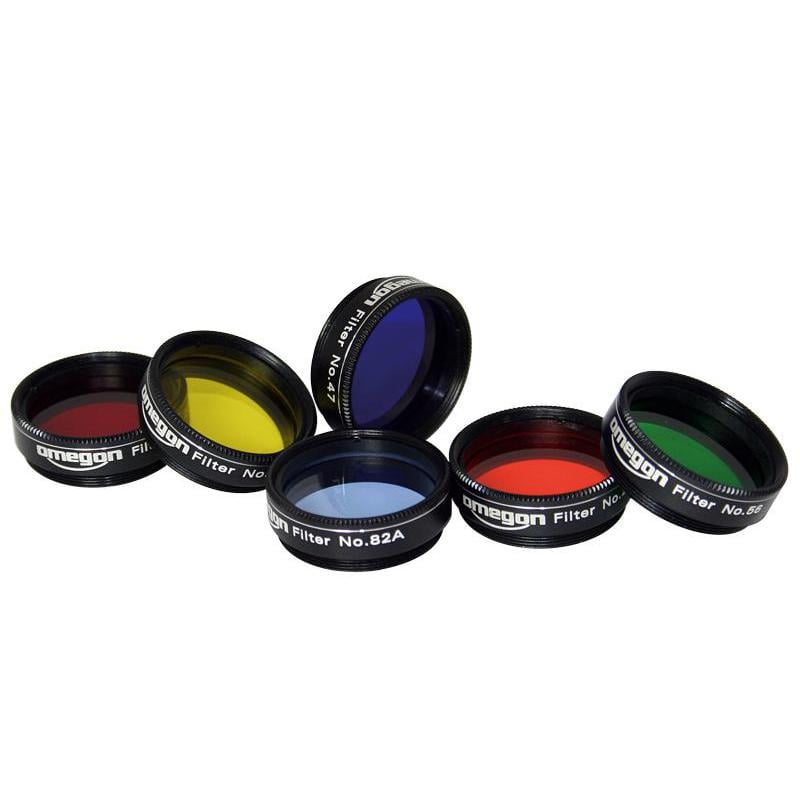

Color filter set with 6 color filters
Other information about the Total Lunar Eclipse and the Mars Opposition is available here:
Infographic: Total Lunar Eclipse on the 27th of June 2018
Mars Opposition 2018: How to Observe Mars and its Details