A solar eclipse after six years, the large planets in opposition and the August meteor shower is visible without any moonlight.
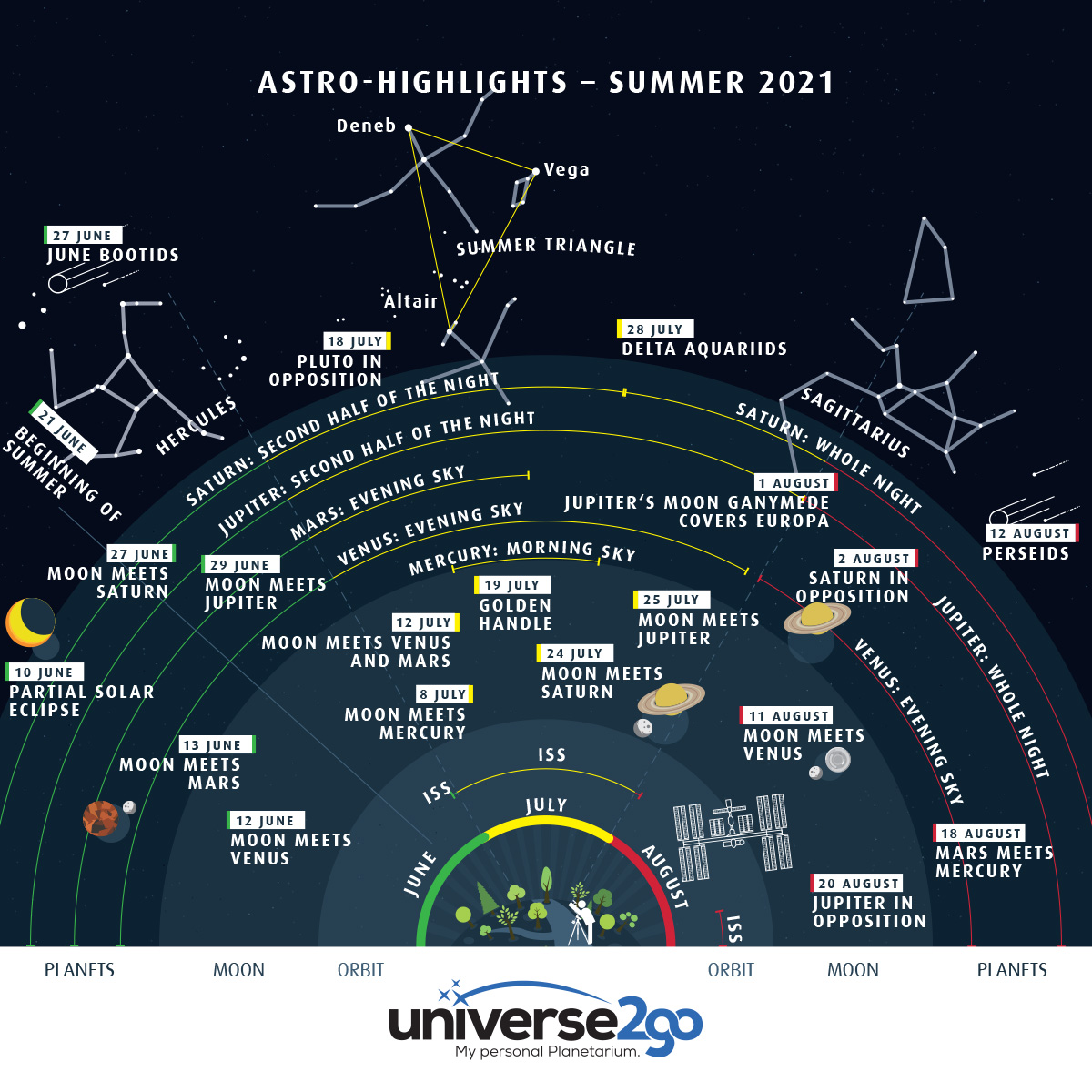
If you’re not looking at the stars this summer, you’re missing something. The sky chart “Astro-highlights – Summer 2021” shows you all the significant celestial events at a glance so that you don’t miss anything. Additional information about these events can be found below the graphic.
We wish you lots of observing pleasure!
June
10/6 Partial solar eclipse
The last partial solar eclipse in Europe was visible on 20 March 2015. The Moon covered up to 80% of the Sun’s disk then. The next solar eclipse occurs on 10 June. It is an annular solar eclipse visible in Greenland and Northern Canada, and partially visible in Central Europe. It is relatively unspectacular, only covering a few percent of the Sun. The further north you are, the higher the degree of the eclipse. In Munich, only 6.3% of the lunar limb touches the Sun, whereas in Hamburg it is 17.3%. The eclipse begins at 11:35a.m. and ends at 13:22 (depending on the exact location). Caution: Only observe the Sun with a suitable solar filter, which you can purchase from our online shop.
Degree of coverage at our Astroshop sites:
Landsberg, Germany: 6.56%
Marseille, France: 2.7%
Malaga, Spain: 1.3%
Warsaw, Poland: 9.9%
Hasselt/Genk, Belgium: 14.9%
Aveiro, Portugal: 9%
Palermo, Italy: 0%
12/6 The Moon meets Venus
The faint waxing crescent Moon and brilliant Venus appear low to the west shortly after sunset. To the upper left, you will discover Mars. If you are observing with binoculars, a short diagonal sweep to the upper left will bring you to the Beehive Cluster M44.
13/6 The Moon meets Mars
Today the Moon rises higher and joins the planet Mars, which it passes at a distance of 1.8 degrees. Both make a beautiful view through binoculars.
27/6 June Bootids
The June Bootids meteor shower originates in the Boötes constellation. The number of falling stars is small but variable. There have been years in which no meteors were sighted at all, but there have also been occurrences of 100 per hour. This meteor shower is exciting and worth taking a closer look at.
27/6 The Moon meets Saturn
Those who want to see the big gas giants will have to wait until midnight in June. Saturn is currently in the constellation of Capricorn, the horned mountain goat that climbs the meridian at the peak of the sky before dawn. The Moon passes Saturn today at a distance of about 9 degrees.
29/6 The Moon meets Jupiter
On its way along the ecliptic this morning, the Moon passes about 5 degrees below Jupiter. The large differences in brightness between the Moon, Jupiter, Saturn and the brightest stars are interesting to observe.
July
8/7 The Moon meets Mercury
Mercury hovers low over the horizon in the morning sky for the next few days. We can observe it with a perfect horizon view well after 4a.m., close above a flat landscape. The crescent Moon joins it 2.5 degrees above. The new Moon is in two days’ time.
12/7 The Moon meets Venus and Mars
As dusk falls, the Moon and the two planets Venus and Mars make for a delightful sight. The pouncing Leo seemingly about to snap at the three objects. You can admire both celestial bodies through binoculars in one field of view. It’s also a great opportunity to take a photo at dusk.
18/7 Pluto in opposition
Pluto is a dwarf planet that is not easily visible and a challenge for larger telescopes. Once the 9th planet, it was stripped of its planetary dignity in 2006, but of course our enthusiasm for the solar system’s outpost remains undiminished. If you want to set your sights on it, the best time to do so is during its opposition. Use your GoTo mount’s controller and a star chart to distinguish it from the background stars.
Coordinates for GoTo controller (23:59 CEST): RA: 19h49m59s, Dec: -22°38′
19/7 Golden Handle
The Golden Handle of the Moon? It does exist, but only during a certain lunar phase. Appearing like a handle of light, it is an effect caused by light on the lunar surface, along the terminator line. We are gazing at the Mare Imbrium in the Sinus Iridum crater region and the Montes Jura. Here, the sun rises at the day-night boundary. While the crater is still in darkness, the peaks of Montes Jura catch the sunlight at their summits. A golden ring in the darkness. Best seen between 18:00 and 21:30 CEST.
20/7 The Moon meets Antares
This evening, the Moon remains to the east of the star Antares. It is a red supergiant and shines bright with a reddish hue in the night sky. Its diameter is 700 times greater than that of our Sun and it would swallow some planets, including our Earth, if it were to take the place of our own celestial body.
21/7 Venus meets Regulus
With a good view of the horizon, you will discover Venus at the foot of the constellation Leo after sunset. In the immediate vicinity you will find the star Alpha Leonis, better known as Regulus. The name means “little King” or “prince”. If you’re thinking of little Simba and the Lion King, you’re probably right.
24/7 The Moon meets Saturn
Shortly before midnight, the constellation of Capricorn appears above the horizon. It is easily recognised by its bowl-like shape. The Moon passes below Saturn at a distance of 4.6 degrees on this night. If you focus on Saturn with binoculars, you will notice a magnitude 5.8 star on your left.
25/7 The Moon meets Jupiter
One day after its encounter with Saturn, the Moon meets Jupiter in the constellation of Aquarius. On this night, the two celestial bodies are separated by 5.5 degrees. Next month, the two gas giants will be in opposition to the Sun.
28/7 Delta Aquariids
The Delta Aquariids are a meteoroid stream that appear to originate in Aquarius. With around 25 meteors per hour, however, it trails far behind the August meteor shower in terms of prominence. Because the Moon phase is very high, the only suitable time for observation is before moonrise.
August
1/8 Jupiter’s moon Ganymede covers Europa
If you take a look through a telescope after Jupiter rises, you will notice the two moons of Jupiter, Europa and Ganymede. Like double stars, they appear close to each other. At 0:00 CEST, Ganymede partially obscures the somewhat smaller Europa, and at around 2:00 CEST, the two moons go their separate ways again.
2/8 Saturn in opposition
Due to the low position of the ecliptic plane, Saturn has remained low above the horizon in recent years. In 2019, it reached a height of about 20 degrees. During its opposition this year, we can observe it at an altitude of 24 degrees. Over the next few years, Saturn will continue to climb higher. The higher its position, the less we have to contend with atmospheric air turbulence.
On 2 August it reaches its opposition and shines brightly in the sky with a magnitude of 0.1. In doing so, it competes with the brightest stars. We recognise it by its yellowish colour and calm glow. Its ring opening is 18 degrees and if we look at the ring system from the north, we can easily identify the Cassini division.
11/8 The Moon meets Venus
A gaze into the evening twilight is well worth it, Venus shines brightly low in the west with the narrow crescent Moon just above it.
12/8 Perseids
Enjoy the most beautiful shooting stars of the year. The Perseids can be seen at their best this year, there will be a new Moon and dark skies all night while we observe them. The meteor shower is most intense during the morning hours of 12 August. At this time, up to 100 shooting stars fall through our atmosphere each hour at a speed of approximately 216,000 km/h. The best observation time is between 22:00 and 4:00 CEST.
18/8 Mars meets Mercury
An extremely close encounter for seasoned observers. At dusk on 18 August, Mars and Mercury meet only about 3 degrees above the horizon. The sun is barely below the horizon at this time.
20/8 Jupiter in opposition
You can already see Jupiter rising flat in the east at twilight, at magnitude -2.8, a bright object that is hard to miss. But the evening sky has even more to offer in terms of conspicuous objects; the moon and Saturn in close proximity and radiant Venus close above the western horizon.
Today, Jupiter draws all the attention – it is in opposition to the Sun and can be admired all night long. It is now separated from Earth by 600 million kilometres and the light takes just over half an hour to reach us. Its apparent diameter is 49″, it reaches its meridian passage and thus its best visibility and highest position at 1:14 CEST.