“Where there’s a lot of light, there’s a lot of shadow”.
These words come from no less than Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. When he wrote these lines, nobody had even conceived of digital cameras. And the famous poet expressed this in a totally different context.
And yet: This sentence is so well suited to astronomy camera sensors that we simply had to use it.
But how does it all fit together? And why does this quote no longer apply to cameras with new Exmor R sensors? We’ll come back to that.
 100% more sensitive cameras by ToupTek
100% more sensitive cameras by ToupTek
This is news that many friends of astronomy will be pleased with: The latest ToupTek cameras are up to 100% more sensitive (source: Sony) than older, conventional CMOS cameras. For recently, great things have been achieved in sensor technology. To put it briefly: Thanks to the new Exmor R sensor, it’s now possible to put even more object information on the chip with short exposure times.
The cameras by ToupTek have already been fitted with these latest, brand-new sensors: Here’s the link to the cameras.
Until a few years ago, people still preferred CCD sensors. This was because they created less noise, were sensitive and you could recognise more details. But CMOS sensors have been improved. Fast data transport and super-fast digitalisation round out the achievements. Noise was markedly reduced, making this technology interesting for astronomy.
These CMOS sensors are also referred to as front-illuminated sensors. And this is where Goethe’s quote: “Where there’s a lot of light, there’s a lot of shadow” becomes interesting. Because it’s got something to do with the architecture or the construction of the chip.
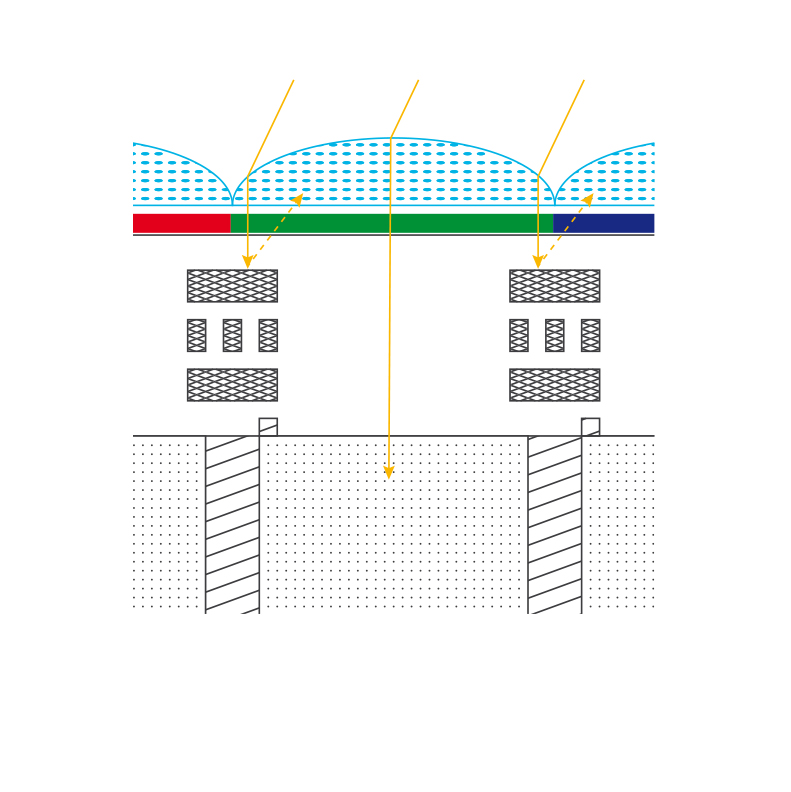 “Classic” CMOS sensors
“Classic” CMOS sensors
Front-illuminated sensors contais quite a few elements that the photons must go through before they reach their target land on the pixel.
First, there are the microlenses, then the colour filters and then finally the electronics. The latter were placed on the chip from above. This means: at this spot, there are aluminium strips, wires and transistors. The photons must go through them, too. After all that, the light finally reaches the long-awaited pixel.
The electronics, however, unfortunately, acts like a shadow-caster. It’s a little like what we experience with telescopes with large secondary mirrors: some of the light is absorbed and diverted.
Some photons simply don’t have a chance. They are not let through or they are simply reflected by the metal wire. This consequence is unavoidable: Less light reaches the sensor.
Sony, however, thought about how current chips could be made more sensitive. And something amazing occurred to them and which is now being used in astronomy cameras: “Back-illuminated” CMOS sensors.
The new “back-illuminated” sensors by Sony
Sony has taken sensors apart and put them back together quite differently. Now, the photons pass through the microlenses and then the colour filters. So far, so good. But after that, they go straight to the pixels.
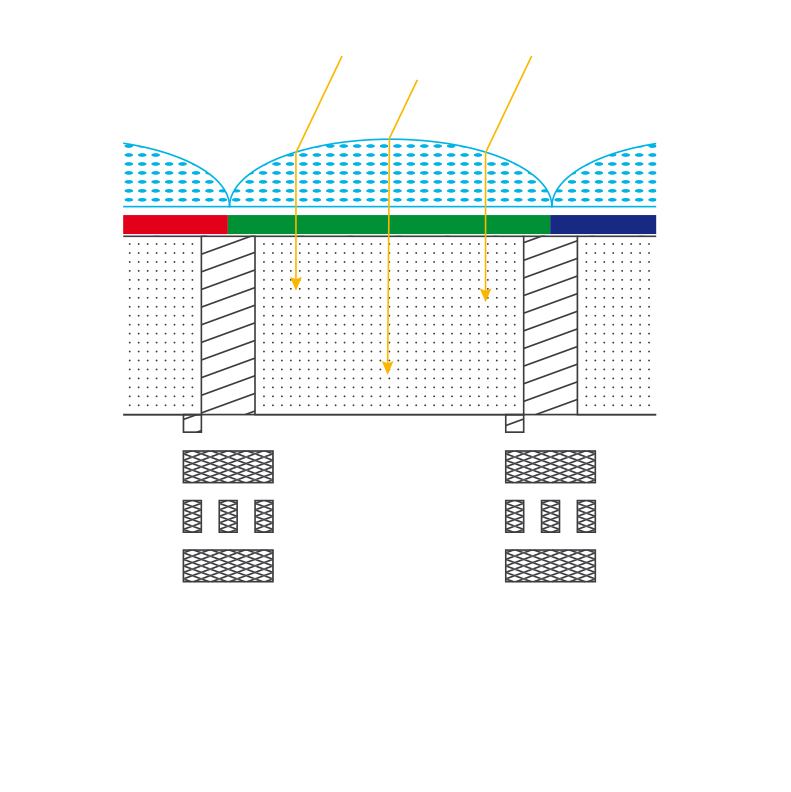 The electronics, wires and transistors are located behind. The photons now reach the photo cells without being diverted. The silicon substrate is illuminated from behind instead of from the front. Another advantage is STARVIS technology, a sub-group of the Exmor R sensors that possess even higher sensitivity. This technology realises its greatest benefit precisely where there is little light.
The electronics, wires and transistors are located behind. The photons now reach the photo cells without being diverted. The silicon substrate is illuminated from behind instead of from the front. Another advantage is STARVIS technology, a sub-group of the Exmor R sensors that possess even higher sensitivity. This technology realises its greatest benefit precisely where there is little light.
Thanks to numerous improvements, the Exmor R sensors are extremely fast , produce even less noise, and are twice as sensitive (source: Sony) and even have higher transmission in the infra-red.
This technology has been used in research for a long time already. But until now, the price of such cameras was astronomically high. Thanks to the fall in price, amateurs can now enjoy the benefits of these CMOS sensors.
What does this mean for your astronomy shots?
- More light in a shorter time
- Shorter exposure times – and therefore fewer problems with tracking
- Galaxies and nebulae can now be photographed without cooled cameras
- Extremely high frame rates – resulting in even sharper planet shots
- Higher sensitivity in the close infra-red range – for images of Mars and Venus
- Brighter celestial objects often possible as live video
Conclusion:
These new “back-illuminated” sensors by Sony offer new and exciting possibilities for astrophotographers. Thanks to the lower costs the prices are low. And the gain is beautiful astronomy photographs with little outlay. But the best of all is: The cameras by ToupTek are already fitted with this technology. Perhaps, we could now say: “Where there’s a lot of light, there remains a lot of light”. At least, as far as these new cameras are concerned.
P.S.:
If you want to use these cameras, too, then go here.
